Helpers
Helpers is just a set of classes who help you make somethings more fast.
Centralize elements
Add class="center"To centralize elements.
Float Elements
Elements can be floated in right or left, add class="right" to float an element to right or add class="left" to float an element to left.
Square Elements
add class="square" to change elements border to Square.
Flex classes
Flex classes are just a set of classes to simplify the use of CSS flexbox layout, is so easy, take a look.
Properties for the parent (flex container).
Flex-direction
class="row" or class="column" Display all the items of container in a row or column. Think of flex items as primarily laying out either in horizontal rows or vertical columns.

Example:
<div class="container row">
<article class="item">Item 1</article>
<article class="item">Item 2</article>
<article class="item">Item 3</article>
<article class="item">Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
row: left to right in ltr; right to left in rtlrow-reverse: right to left in ltr; left to right in rtlColumn or col-reverse: same as row but top to bottomColumn-reverse or col-reverse: same as row-reverse but bottom to top
Flex-wrap
class="wrap" or class="nowrap". By default, flex items will all try to fit onto one line. You can change that and allow the items to wrap as needed with this classes.

Example:
<div class="container wrap">
<article class="item">Item 1</article>
<article class="item">Item 2</article>
<article class="item">Item 3</article>
<article class="item">Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
nowrap or nobreak: all flex items will be on one linewrap or break: flex items will wrap onto multiple lines, from top to bottom.wrap-reverse or break-reverse: sflex items will wrap onto multiple lines from bottom to top.
Flex-alignment
class="center-align" or class="left-align" or class="right-align". This defines the alignment along the main axis. It also exerts some control over the alignment of items when they overflow the line.
Example:
<div class="container row right-align">
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 1</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 2</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 3</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
left-align or justify-start: items are packed toward the start line.right-align or justify-end: items are packed toward to end line.center-align or justify-center: items are centered along the line.
Flex-spacing
space-between or space-around or space-evenly. It helps distribute extra free space left over when either all the flex items on a line are inflexible, or are flexible but have reached their maximum size.
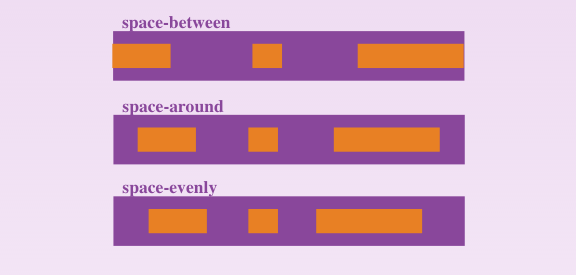
Example:
<div class="container row space-between">
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 1</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 2</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 3</article>
<article class="item" style="width: 100px;">Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
space-between: items are evenly distributed in the line; first item is on the start line, last item on the end line.space-around: items are evenly distributed in the line with equal space around them. Note that visually the spaces aren't equal, since all the items have equal space on both sides. The first item will have one unit of space against the container edge, but two units of space between the next item because that next item has its own spacing that applies.space-evenly: items are distributed so that the spacing between any two items (and the space to the edges) is equal.
Flex-align-items
class="middle-align" or class="bottom-align". This defines the default behaviour for how flex items are laid out along the cross axis on the current line. Think of it as the flex-alignment version for the cross-axis (perpendicular to the main-axis).
Example:
<div class="container row middle-align" style="height: 300px;">
<article class="item" >Item 1</article>
<article class="item" >Item 2</article>
<article class="item" >Item 3</article>
<article class="item" >Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
top-align or align-items-start: Cross-start margin edge of the items is placed on the cross-start line.middle-align or align-items-center: Items are centered in the cross-axis.bottom-align or align-items-end: Cross-end margin edge of the items is placed on the cross-end line.baseline or baseline-items: Items are aligned such as their baselines align.stretch or stretch-items: Stretch to fill the container (still respect min-width/max-width)
Flex-align-content
This aligns a flex container's lines within when there is extra space in the cross-axis, similar to how flex-alignment aligns individual items within the main-axis.
Note: this property has no effect when there is only one line of flex items.
Example:
<div class="container row wrap content-top" style="height: 400px;">
<article class="item" >Item 1</article>
<article class="item" >Item 2</article>
<article class="item" >Item 3</article>
<article class="item" >Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
content-top or col-top: lines packed to the start of the container.content-bottom: lines packed to the end of the container.content-center: lines packed to the center of the container.content-space-between: lines evenly distributed; the first line is at the start of the container while the last one is at the end.content-space-around: lines evenly distributed with equal space around each line.content-stretch: lines stretch to take up the remaining space.
Flex items
Properties for the Children (flex items).
Order
class="order-number". By default, flex items are laid out in the source order. However, the order property controls the order in which they appear in the flex container.

Example:
<div class="container row wrap">
<article class="item order-4" >Item 1</article>
<article class="item order-3" >Item 2</article>
<article class="item order-2" >Item 3</article>
<article class="item order-1" >Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
order-1...10: Defines the order of flex-items within container.
Flex-grow
class="grow-number". This defines the ability for a flex item to grow if necessary. It accepts a unitless value that serves as a proportion. It dictates what amount of the available space inside the flex container the item should take up.
If all items have flex-grow set to 1, the remaining space in the container will be distributed equally to all children. If one of the children has a value of 2, the remaining space would take up twice as much space as the others (or it will try to, at least).

Note: Negative numbers are invalid.
Default Classes
grow-1...10: This defines the ability for a flex item to grow if necessary..
Flex-shrink
class="shrink-number". This defines the ability for a flex item to shrink if necessary.
Note: Negative numbers are invalid.
shrink-1...10: This defines the ability for a flex item to shrink if necessary..
Flex-align-self
class="self-position" or class="align-self-position"This allows the default alignment (or the one specified by align-items) to be overridden for individual flex items.
Note: float, clear and vertical-align have no effect on a flex item.

Example:
<div class="container row" style="height: 400px;">
<article class="item self-center" >Item 1</article>
<article class="item self-bottom" >Item 2</article>
<article class="item" >Item 3</article>
<article class="item" >Item 4</article>
</div>
Default Classes
self-top or align-self-topself-bottom or align-self-bottomself-center or align-self-centerself-baseline or align-self-baselineself-stretch or align-self-stretch
Issues
Bug or features request? Open an Issue